Block Level File Sync
Cloud computing services are slowly becoming an integral part of our lives. Companies and individuals use it to collaborate, store their files and for so much more. The cloud makes our lives easier. It makes the internet more pleasurable to use. As users, it is not important to understand how things work beneath the hood. But knowing a little can help as there are a lot of service providers out there, and one will have to choose. In this article, you’ll learn how block level file sync works. This is becoming an integral concept in cloud computing, so you’ll find such knowledge helpful even as a user.
What you’ll learn:
- What is Block Level Sync?
- What Does Block Level Sync Do?
- How is Block Level File Sync Used?
- The Alternative to Block Level Sync
- Why Care About Block Level Sync?
- Where Block Level Sync is Commonly Used?
- How to Check for Block Level Sync?
- Pros and Cons
What is Block Level File Sync?
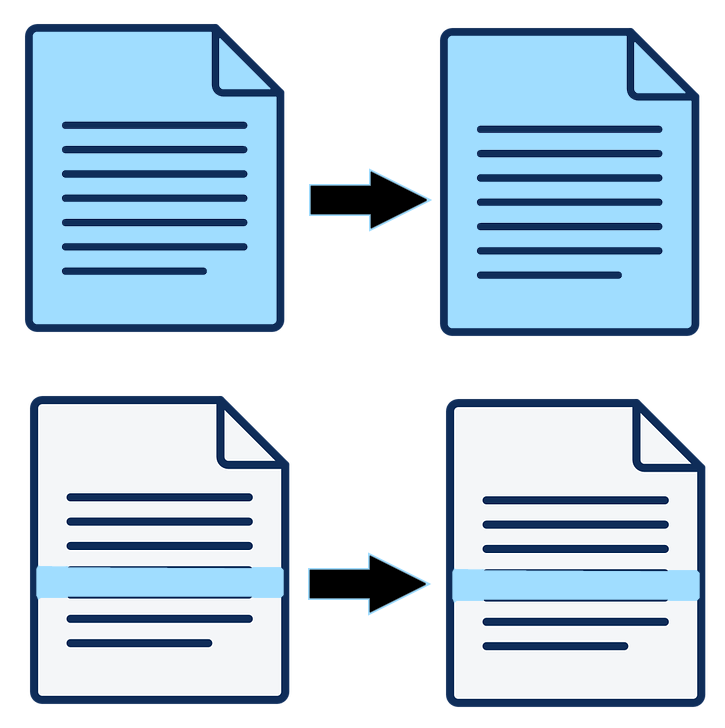
Block level file sync is a method for file transfer in cloud computing. It involves the transfer of blocks of a file, as opposed to the entire file. Take, for example, a 1GB file which synchronizes with the cloud. The convention will be to transfer the entire file i.e. 1GB. But with block level file sync, only the block of interest gets transferred. Block of interest, in this case, is the block that matches the part of the file you changed. When synchronizing, just the block that experienced a change gets transferred.
What Does Block Level File Sync Do?
File synchronization makes cloud computing powerful. You can change a file, and the changes get updated in the cloud storage. So when you work on another device, you can access the changes. What block level sync does is that it uploads the block you change alone, instead of uploading the entire file.

How is Block Level File Sync Used?
The cloud storage service providers are the ones who implement block level sync. Hence, it is not in your hands to get it to work. These providers have various reasons for their choices. So it shouldn’t be surprising that not all of them make use of block level file sync.
For block level file sync to work, you need to upload the file first. Hence, if it’s a 1GB file, the entire file has to be sent to the cloud. Thereafter, the file sync kicks in and only the modified block gets synchronized instead of the entire file. So if a 20MB block gets modified, then that’s all the cloud service provider pulls from your device, not 1GB.
The Alternative to Block Level Sync
Block level file sync is not the only method for synchronization on all cloud storage services. There is one common alternative, which is arguably the only one. The file-level synchronization. Unlike the block level file sync which only transfers the changed blocks of a file, the file-level sync transfers the entire file. This comes with its own advantages, as it allows for complete file encryption. Here, the cloud service provider has zero knowledge of the contents of the file as only the user has the key to it.
While the file-level sync may look like a terrible decision since it uploads the entire file, it has its upsides. One of which is that the initial upload time is shorter when compared to that for block level file sync. Once again, it is not in the hands of the user to choose. The only exception is where the cloud service provider offers an interface for users to do so.
Why Care About Block Level Sync?
Yes, block level sync is very useful in cloud computing. But why should you care about it? Well, since many people will use a cloud service at some point, it is important to understand its impact.
Here are some reasons why you should care about it:
- It Impacts Data Usage: When a cloud service uses block level file sync, they take snapshots of the file. Then they compare the hash to check for changed blocks of that file. During the synchronization process, just this block gets uploaded, and it consumes less bandwidth.
- It Impacts Synchronization Speed: Since only the modified block gets uploaded, the upload time becomes shorter. Because of this, you need not make use of a fast internet connection as slow ones will work just fine too.
- It Impacts Encryption: For a cloud service provider to implement block file sync for a file; they require access to the file. That’s the only way they can know what blocks you change. As a result, the entire file cannot be encrypted such that the provider has zero knowledge of this file.
Where is Block Level Sync Commonly Used?
Block level sync is commonly used by cloud service providers that allow you to change files on-the-go. So you have a document and want to make changes, these providers will let you make your edits and then synchronize.
Hence, you will often find cloud services that only let you upload and secure your files using file-level sync. This explains why a service like Dropbox uses block level sync, while Sync.com doesn’t.

How to Check for Block Level Sync?
When a cloud service uses block level sync, the first upload will usually take a while. The upload time is often longer than you will experience when using a service with file-level sync. However, after the first upload, the modifications will take a shorter time to upload. When comparing this second case, the block level sync will upload a lot quicker than the file-level sync.
So you can know if a service uses block level sync by comparing the time to upload a file for the first time with the subsequent times. If it takes a shorter upload time subsequently, then it is most likely block level sync in action. Otherwise, the service uses a file-level synchronization method.

Pros and Cons
The Pros
There are some advantages that come with using block level sync. Some of them are:
- Faster uploads: It uploads only the modifications to the cloud. So the uploads are faster than you’ll get from file-level sync.
- Lesser data usage: The modified blocks are lesser, so the uploads don’t consume a lot of data.
- Seamless collaboration: When multiple people are working on a single file, it is normal for the file to change a lot. Since the blocks of changes upload immediately, the collaborators can see the modifications almost instantly.
- Enables document versioning: When working on a document or a file, you often will want to check older versions of that document. The blocks upload as you make changes, making it is possible to return to previous versions of that file. Regular file sync also enables this.
The Cons
Here is the main disadvantage of block level sync:
- Security and Consistency Issues: There may often be issues when uploading files to cloud services that use the block-level sync method. Encryption methods may have glitches and the files may have inconsistent versions. Client-side encryption is not possible with block level sync.
Conclusion
Block level file sync is important for seamless collaboration through cloud services. It has huge benefits, and cloud service providers are beginning to implement it in their products. But block level file sync also means you’ll never have true file protection & privacy since client-side encryption isn’t possible. You’ve learnt a lot about this technology in this article, and should be able to figure out if a service uses it or not. Check out my cloud storage recommendations down below.
What are your thoughts on the best block level file sync? Let us know down below!
