
4 Types Of Hard Drives
Throughout the years, we have been quite obsessed about how to make the storage of data become more efficient and effective. Various companies in the field of information technology are working tirelessly to develop the best system in storing computer data. While USB flash drives, SD cards, cloud storage, optical media storage, and cloud backup solution have been invented and have recently become popular, one piece of fact still remains. All of our desktop computers and laptops mainly rely on hard disks in order to store computer data. This is the reason why we are going to discuss the 4 types of hard drives. We are going to uncover what each of the types of hard drives can do and explore what is the most efficient type of hard drive we should use.
Types of Hard Drives # 1: Small Computer System Interface (SCSI)
Today’s generation may not be aware of the Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) as one of the earlier versions and types of hard drives. It was actually first released in the 1980s and was first named to be Shugart Associates System Interface (SASI). The first version actually consists of a flat ribbon connector with 50 pins embedded on it which allows hard disk drives to be attached to a computer. It allows approximately 7 to 15 different devices to be connected to a single motherboard. The SCSI as a type of hard drive has been adopted by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in the 1990s. Since then, various versions based on the previous SCSI hard drive technology have been released.
Based on research, the modern model of SCSI can transmit data up to 80 MB per second. Looking at the perspective of our modern world, SCSI hard drives are very slow in terms of data transmission. The said hard drive technology is now obsolete and has been replaced by other types of hard disks that are more efficient and reliable.

Types of Hard Drives # 2: Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment
The Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment system as one of the types of hard drives that existed is considered to be a more reliable and faster hard drive type than the SCSI. It was actually developed in the year 1986 by a company called Western Digital. There are actually variations to the name of PATA. It can also be called Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) or Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics (EIDE) drives. Earlier versions of the PATA hard drives use a cable that has 40 wires attached to a 40-pin connector. The latest models of the PATA drives have 80 wires attached to an 80-pin connector.
Unlike SCSI which has a maximum data transfer speed of only 80 MB per second, the PATA hard drives can transmit data as fast as 133 MB per second. This is approximately 66.25% improvement in terms of data transmission for this type of hard drive technology when compared to SCSI. You can connect a maximum of 4 PATA drives in a single motherboard. While it is a better option than the SCSI hard drive, PATA hard drive is also now considered to obsolete at this point in time. You will really have a hard time finding this type of hard drive nowadays.
Types of Hard Drives # 3: Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
The PATA drives have been replaced by the SATA drives. As a matter of fact, if you look at most of the desktop computers and laptops that are available today, you will see that these computers are now using SATA hard drives. This is because SATA hard drives are faster and more reliable than PATA drives. In terms of data transmission, 2.5” SATA hard drives can deliver a speed of 150 MB per second. There are newer versions of the 3.5” SATA Hard disk drives than can transmit data as fast as 200 MB per second. If we base it on maximum speed, it is approximately 50.38% improvement on data transmission speed compared to PATA hard drives.

There has been preferential treatment to SATA hard disk drives because of the affordability of this particular type of hard drive. Just like PATA drives, the SATA drives stores data by using the concept of magnetism on rotating disk. Since there are lots of moving parts involved in the mechanism of this particular type of hard drive, it is more prone to mechanical failure. The wear and tear process is applied faster in SATA HDD than in the SSD. As a matter of fact, one of the biggest disadvantages of the SATA drive is that it is easily destroyed when your laptop computer falls hard on the ground. The moving parts of the SATA drive will no longer function properly if a strong force is applied to the mechanism.
If you want to back up your data coming from your Hard Disk Drives to protect it in case of mechanical failures, then I suggest you look at the table below since it lists down all the possible cloud backup solutions that are efficient and reliable.
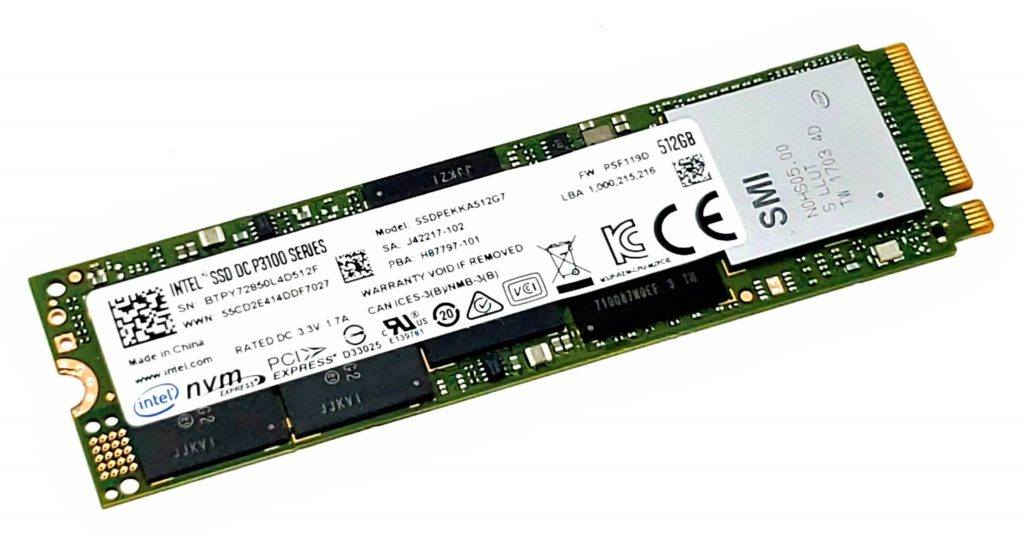
Types of Hard Drives # 4: Solid State Drive
The problem of mechanical failure in SATA Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) initiated the development of an alternative computer data storage model. As a matter of fact, it became the reason why Solid State Drives (SSDs) were invented. This type of hard drive solves the problem by actually storing data on semiconductor chips. In this way, there will no longer be a need for rotating magnetic disks that are prone to mechanical failure. Instead of having a consistently moving and rotating read-write head, the SSD is made up of electrical components as well as transistors that are usually used on a semiconductor chip.
Because of the compact design of SSDs, it allowed faster data transmission. In fact, a SATA 3.0 type of SSD can have a maximum data transfer speed of 550 MB per second. If you compare it with the traditional SATA Hard Disk Drive (HDD), you will see that it has a remarkable 175% increase in terms of data transmission for SSDs. That’s close to 3 times the maximum data transfer speed of SATA HDD. What is more impressive is that PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) SSD can have a maximum data transfer speed of 3000 MB per second. That’s actually 15 times faster than the traditional SATA HDD.

3 Things to Consider In Choosing the Best Type of Hard Drive
There are actually various considerations you should look into when choosing the best type of hard drive available in the market today. First, you should look into the data transmission speed. Second, you should consider the cost and affordability of the various types of hard drives. Third, you should consider the reliability and lifespan of the various types of hard drives.
- Data Transmission Speed
Data transmission speed is one of the most important factors when choosing the best type of hard drive. If you are dealing with large files of data, then the SSD hard drive is the best option for you. The SATA 3.0 SSD is more common than the PCIe SSD and is more widely available in the market today. The SATA 3.0 SSD can give you a maximum data transfer speed of 550 MB per second whereas the SATA HDD can only give you a maximum data transmission speed of 200 MB per second. In this particular consideration, SSD works better than the traditional HDD.
- Cost & Affordability
There is a huge difference between the cost of an HDD and the SSD. It is always cheaper to buy the HDD than the SSD. As a matter of fact, based on the studies conducted by people analyzing the computer data storage industry, SSD is 4 times more expensive than the HDD. So if the price is an issue to you, then I suggest you just use the SATA HDD which is the most common hard disk drive being currently used in laptops and desktop computers.
- Reliability & Lifespan
In terms of reliability and lifespan, SSD ranks higher than HDD. In terms of file opening speed, reports suggest that it is 30% faster to open a file in an SSD than in the HDD. Aside from that, SDD is less vulnerable to data loss due to magnetism. SSD is literally protected against the effects of outside magnetism. HDD is more vulnerable to mechanical failure due to its moving parts. HDD is also more vulnerable to jolts and vibrations which causes the system to be easily destroyed.
However, you should also be aware that SSD is more vulnerable to sudden power outages. This is the reason why newer versions of SSD now have power loss protection mechanisms in place. Even without power, HDD can retain the data stored for a very long time. This is the reason it is better to use HDD for archiving data. But in the case of SSD, once you left it with no power for 2 years, it will start losing parts of the stored data depending on the temperature of the location.
